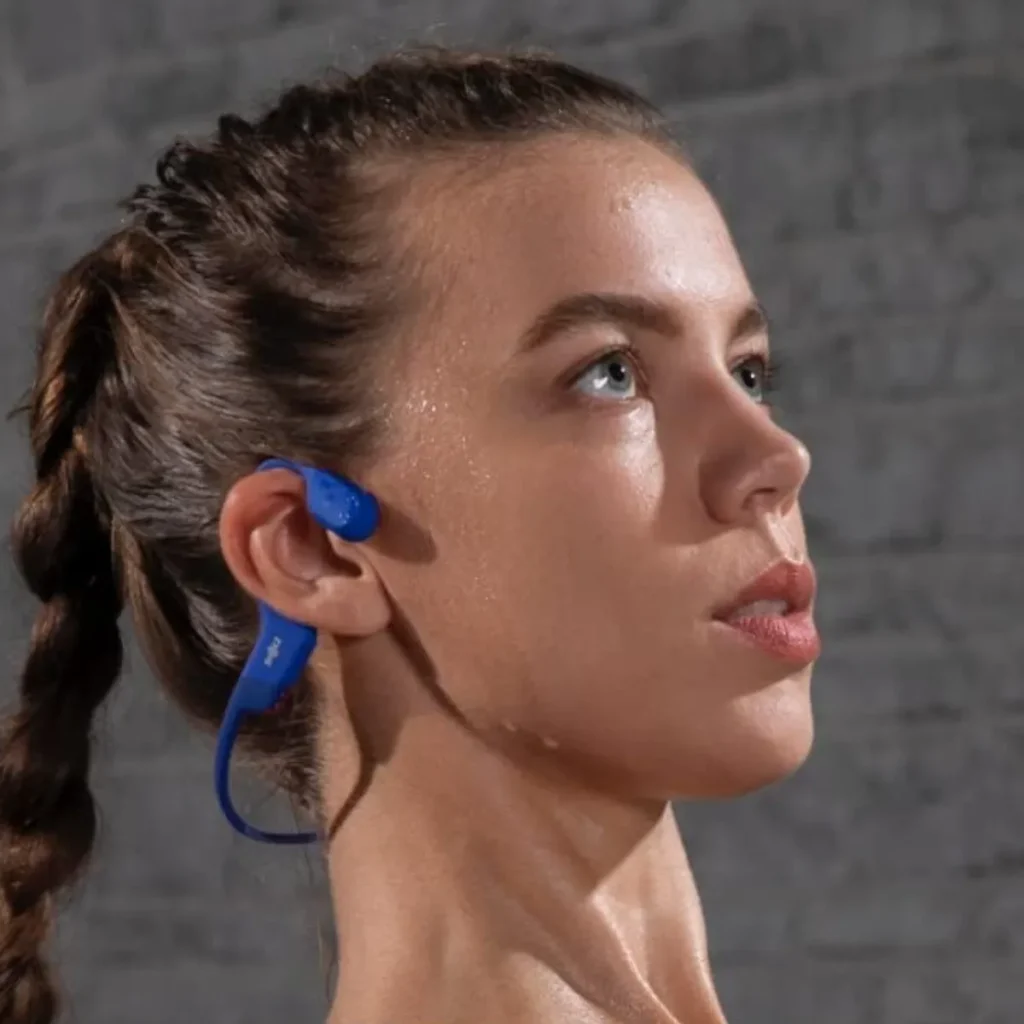
In recent years, sleep technology has seen rapid innovation, but one area making particularly striking progress is bone conduction. Originally developed for hearing aids and military communication, this non-invasive audio transmission method is now being integrated into sleep devices to improve rest, address sleep disorders, and offer more personalized nighttime experiences.
Bone conduction sleep technology works by transmitting sound vibrations directly through the bones of the skull, bypassing the eardrum entirely. These vibrations travel to the cochlea, allowing the user to perceive audio even when their ears are unobstructed or at rest. This method enables devices to deliver sound with minimal disruption to others, making it ideal for shared sleeping spaces or quiet environments.
A Quiet Revolution in Sleep Tech
The integration of bone conduction into sleep technology opens up new possibilities beyond traditional audio playback. While many are familiar with sleep sound machines or noise-canceling headphones, these often come with limitations such as discomfort during sleep, disturbance to partners, or even ear fatigue. Bone conduction offers a more discreet and comfortable alternative.
In particular, manufacturers have begun releasing bone conduction headbands and pillow-integrated devices that allow users to listen to calming music, white noise, guided meditations, or even cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) tracks throughout the night. Because the technology does not block the ears, users remain aware of their surroundings—a feature appreciated by parents, night shift workers, and individuals with safety concerns.
Practical Applications: More Than Just Sound
One of the most exciting aspects of this innovation lies in its therapeutic potential. Devices using bone conduction are being tested for use in treating insomnia, sleep apnea, and other neurological sleep disturbances. For example, startups are experimenting with biofeedback-enabled headbands that use bone conduction audio to guide the user through relaxation techniques when stress-induced wakefulness occurs.
Some devices now incorporate real-time sleep tracking and adaptive sound delivery. These systems can monitor the user’s brainwaves or breathing patterns and adjust audio stimuli to aid deep sleep or gently rouse the user from light sleep, mimicking natural wake cycles. This technology presents a less jarring alternative to traditional alarms and has already gained popularity among people with hearing impairments.
From Labs to Bedrooms: Market Adoption and Progress
The consumer market is increasingly receptive to wearable sleep aids, and bone conduction has begun to carve out a niche. Companies like Kokoon, SleepPhones, and even AfterShokz—previously known for sports headphones—have dipped into sleep-focused bone conduction devices. These products often come in the form of ergonomic headbands or pillow inserts and are designed with comfort, wireless charging, and all-night battery life in mind.
Furthermore, collaborations between sleep researchers and tech developers have led to the creation of clinical-grade devices aimed at both home users and healthcare providers. Some bone conduction sleep aids are now being used in clinical trials to test their effectiveness in enhancing REM sleep or improving recovery in patients with neurological conditions such as PTSD or chronic insomnia.
Addressing Sleep Disorders and Cognitive Health
A significant area of research involves leveraging bone conduction technology to address circadian rhythm disruptions and cognitive dysfunctions. Studies have shown that targeted audio stimulation—especially during slow-wave sleep—can enhance memory consolidation and improve mental performance. By integrating bone conduction delivery with AI-based monitoring, these devices can play specific sounds at optimal moments in the user’s sleep cycle, increasing the impact without causing arousal.
Additionally, for individuals with conditions like tinnitus, bone conduction offers a novel method of providing sound therapy without the intrusive nature of earbuds or speakers. These subtle sounds, often customized through mobile apps, can mask the ringing sensation and promote sleep continuity.
Challenges and Ongoing Research
Despite its promise, bone conduction sleep technology still faces several hurdles. Ensuring consistent contact between the device and the user’s skull during various sleep positions can affect audio quality. Manufacturers are investing in more flexible, form-fitting materials that maintain bone contact without causing discomfort or pressure.
Battery life and heat generation during long usage periods are also being refined. Since sleep typically spans six to eight hours, devices must remain functional and comfortable throughout the night. Companies are addressing this through low-energy Bluetooth protocols, lightweight batteries, and breathable materials.
Moreover, while anecdotal reports from users are positive, more peer-reviewed clinical trials are needed to fully validate the technology’s therapeutic claims. Universities and sleep institutes across the U.S., Europe, and Asia have started multi-year studies to assess the physiological and neurological benefits of bone conduction sleep stimulation.
What the Future Holds
Looking ahead, experts believe bone conduction could be integrated with other biometric sensors to offer comprehensive sleep health solutions. We may see devices that not only play audio but also track oxygen saturation, heart rate variability, and temperature—creating a full picture of an individual’s sleep profile.
Smart homes could also play a role. Sleep devices might sync with lighting systems, thermostats, and smart alarms to create adaptive sleep environments. For example, a bone conduction headband could detect restlessness and trigger changes in room lighting or air circulation to restore sleep quality.
Additionally, there’s growing interest in using bone conduction to support lucid dreaming therapy or manage night terrors through gentle sound cues—opening new therapeutic frontiers in mental health.
A Technology Built for the Silent Hours
Bone conduction sleep devices combine science, innovation, and personalization to offer a silent yet powerful alternative in the sleep tech landscape. As awareness of sleep’s impact on physical and mental well-being continues to grow, tools that provide non-invasive, comfortable, and effective support will gain greater relevance.
From helping users fall asleep faster to supporting mental health and reducing sleep interruptions, bone conduction is no longer limited to audiophile gadgets or military headsets. It’s quietly entering bedrooms—and revolutionizing the way we rest.