Google Agrees to Cut AI Data Centre Power Use to Ease U.S. Grid Strain
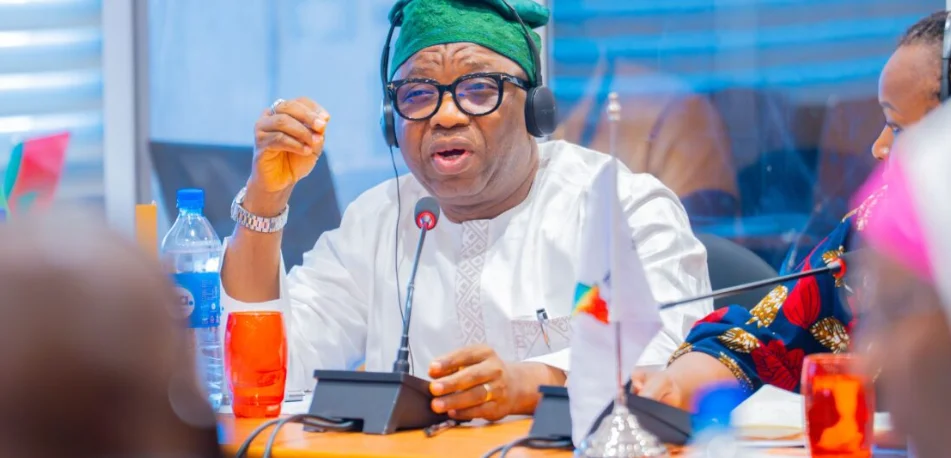
In a groundbreaking move to address growing electricity demand in the U.S., Google has agreed to reduce power usage at its AI data centres during peak periods. This marks the company’s first formal participation in demand-response agreements with electric utilities, a strategy traditionally used by heavy industries to support grid stability.
Google Signs Demand-Response Deals with U.S. Utilities
Under the new agreements, Google will work with Indiana Michigan Power and Tennessee Power Authority to temporarily reduce power consumption at its data centres when requested by the utilities. These efforts aim to free up space on the grid during peak energy demand, minimising the risk of blackouts and skyrocketing bills for households and businesses.
According to Google, the deal will help:
- Accelerate the connection of large data loads to the grid
- Decrease the need for new power plants and transmission lines
- Improve the efficiency of grid management
“It allows large electricity loads like data centers to be interconnected more quickly… and helps grid operators more effectively and efficiently manage power grids,” the company said in a blog post.
AI Expansion Meets Grid Limitations
The initiative comes as AI technology continues to drive massive electricity demand, with machine learning workloads consuming large amounts of energy. The surge has put pressure on U.S. energy infrastructure, already strained by climate challenges and increasing urbanization.
Google’s willingness to reduce power use highlights a growing concern among tech giants: balancing AI innovation with environmental and infrastructural realities.
Demand-Response Programs Reach Big Tech
Demand-response programs, in which energy-intensive businesses agree to scale back usage during peak hours, have long been adopted by manufacturing sectors and crypto miners. In return, companies often benefit from reduced energy bills or financial incentives.
Google’s entry into this space represents a new chapter for the technology industry, especially as energy demand from AI data centers continues to rise.
While financial details of the deals remain undisclosed, analysts say the move sets a precedent for how AI workloads might be regulated and optimized in the near future.
What This Means for the Energy Sector
As the U.S. electricity supply tightens, demand-response arrangements like Google’s may become more widespread. Energy experts predict that tech companies will increasingly need to collaborate with utilities to ensure reliable access to power while supporting grid resilience.
While these agreements currently apply to only a small portion of total grid demand, they may serve as a model for future energy policy and AI infrastructure planning.