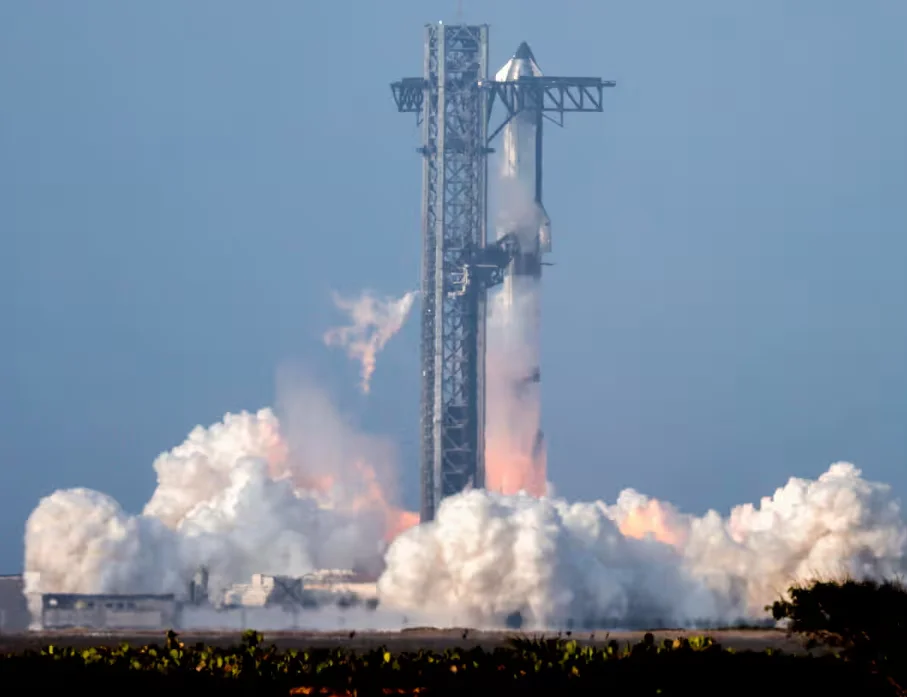
SpaceX’s highly anticipated Starship test flight ended in failure on Tuesday after the massive rocket system lost control in space, marking a fresh obstacle in Elon Musk’s ambitious plans to make life multiplanetary. Despite passing previous failure points, Starship spiralled out of control roughly 30 minutes into the mission, failing to meet critical test objectives.
What Happened During the Starship Launch?
The 400-foot (122-meter) Starship rocket lifted off successfully from SpaceX’s Starbase facility in Boca Chica, Texas. This mission marked the ninth full test flight of the Starship system and the first time a previously flown booster was reused, a major milestone in SpaceX’s push for rocket reusability.
As the upper stage soared into suborbital space, early indicators appeared positive. However, the launch soon took a turn when SpaceX lost contact with the 232-foot lower-stage Super Heavy booster. The booster was intended to perform a controlled splashdown but instead crashed into the sea.
Starship Spins Out of Control in Space
Shortly after booster separation, Starship’s upper stage entered an uncontrollable spin in space. This occurred after a failed attempt to deploy eight test Starlink satellites using a dispenser mechanism like a “Pez candy dispenser.” SpaceX commentator Dan Huot acknowledged on the company’s livestream that “a lot of our on-orbit objectives” were not met.
Elon Musk’s Response and Next Steps
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk, who was expected to speak live at Starbase following the launch about “The Road to Making Life Multiplanetary,” remained silent in public appearances hours after the incident. However, Musk did post an update on X (formerly Twitter), confirming that a fuel tank leak was responsible for the loss of control in space.
“Lot of good data to review,” Musk posted. “Launch cadence for the next 3 flights will be faster, at approximately 1 every 3 to 4 weeks.”
Design Upgrades and Future of Starship
According to SpaceX, the Starship prototype used in this flight featured significant design upgrades compared to earlier versions. These enhancements are part of a broader goal to develop a multi-purpose rocket system capable of:
- Launching massive batches of Starlink satellites
- Supporting lunar missions
- Ferrying astronauts to Mars
Despite the mission’s failure, SpaceX continues to maintain its rapid development pace. The company has committed to accelerating the launch cadence, with the next Starship missions expected every three to four weeks.
What This Means for SpaceX’s Mars Vision
The failure underscores the challenges of building the world’s most powerful and complex rocket system. With each test flight, SpaceX gathers data that informs design improvements. Still, persistent technical setbacks, such as this latest incident, highlight the difficulty of achieving Elon Musk’s long-term vision of colonising Mars.